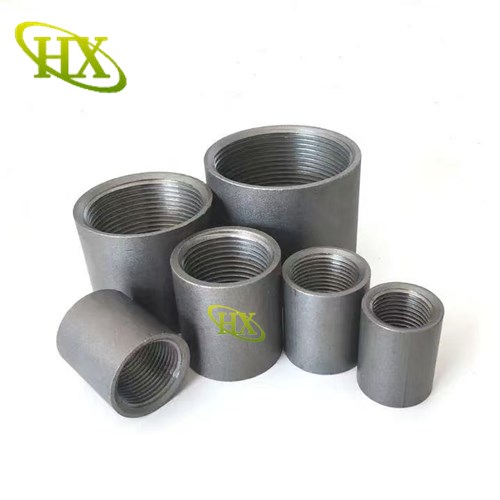
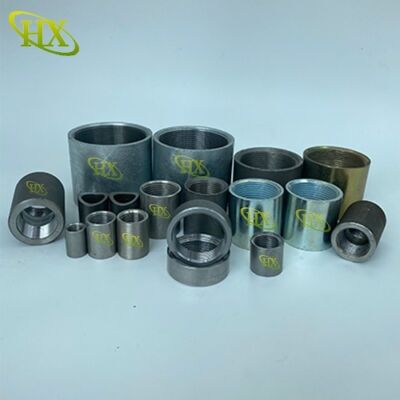
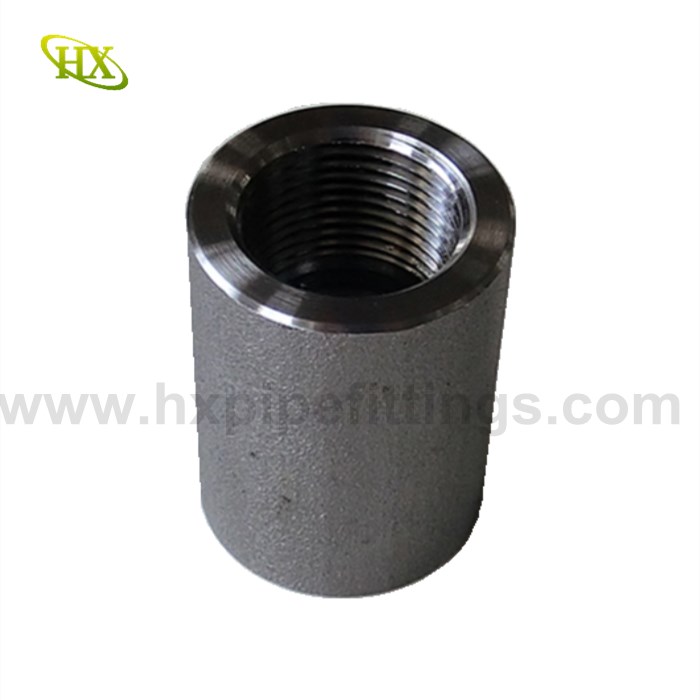
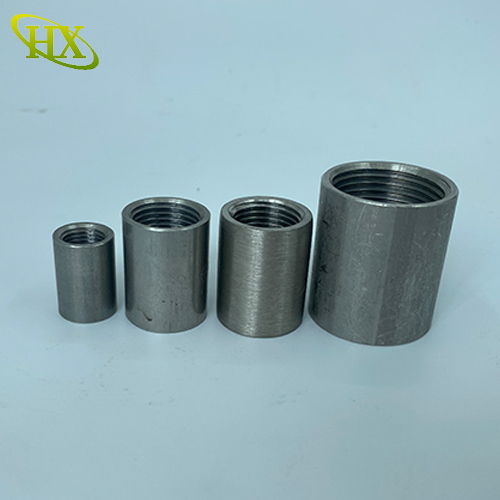
Pipe couplings (also called pipe connectors or steel pipe socket) are essential fittings used to join two pipes of the same or different diameters. These short connecting pieces typically feature female threads or sockets on one or both ends, allowing for secure and leakproof connections.
Pipe couplings serve multiple purposes, including:
Extending or terminating pipelines
Connecting pipes of different sizes (using reducer couplings)
Repairing damaged or leaking pipes
Facilitating directional changes in piping systems
Since most piping installations require multiple sections to navigate obstacles or changes in direction, couplings provide a reliable and efficient solution while maintaining structural integrity.
- Common Materials Used in Pipe Couplings
The material of a pipe coupling directly impacts its durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific environments. Below are the most widely used materials:
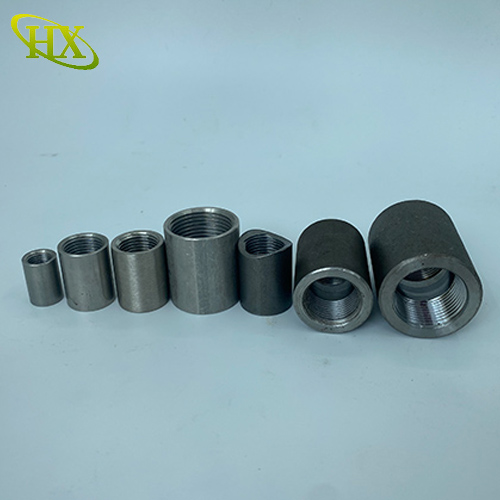
Made from 304 or 316 stainless steel (316 offers superior resistance to chlorides and acids).
Highly corrosionresistant, making them ideal for chemical plants, marine applications, and food processing.
Can withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions.
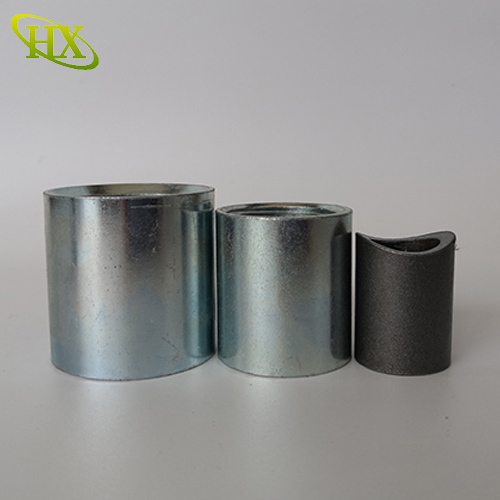
Coated with a zinc layer for enhanced rust prevention.
More affordable than stainless steel but requires periodic inspection in water systems.
Commonly used in outdoor plumbing, irrigation, and lowcost industrial piping.
Black Steel Couplings
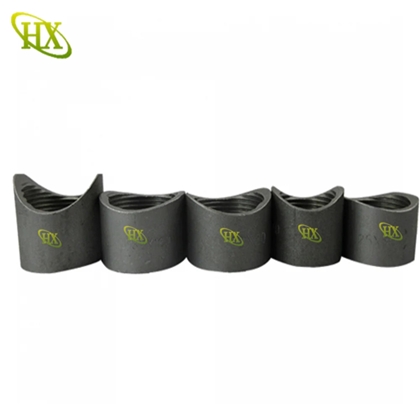


Treated with a black oxide coating for mild corrosion resistance.
Economical and durable but needs additional protection in moist or corrosive environments.
Often used in gas lines and lowpressure industrial systems.
PVC Couplings
Lightweight, chemicalresistant, and easy to install using PVC cement.
Ideal for drainage, irrigation, and lowpressure plumbing.
Typically lasts 10+ years with minimal maintenance.
- Key Features of Pipe Couplings
Flexibility – Available in rigid or flexible designs, depending on movement requirements.
Diameter Adjustment – Reducer couplings allow connections between pipes of different sizes.
MultiPort Options – Tshaped or crossshaped couplings can join three or more pipes.
Angled Designs – Elbow couplings help change pipeline direction without additional fittings.
- Different Types of Pipe Couplings
Full Coupling
Connects two pipes of the same diameter with threaded ends.
Ensures a leakproof seal in smallbore piping systems.
Often used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Half Coupling
Used for branching off from a main pipe or tank.
Only one threaded end, while the other is welded or flanged.
Common in industrial and largediameter piping.
Reducer Coupling
Joins pipes of different sizes (e.g., 1inch to ¾inch).
Essential in systems where smaller feeder lines connect to larger mains.
Compression Coupling
Uses a ferrule and nut to create a tight seal without threading.
Ideal for quick repairs and temporary installations.
- Advantages of Using Pipe Couplings
Prevents Leaks – Tight seals ensure system integrity, even under high pressure.
CostEfficient – Eliminates the need for welding, reducing labor and material costs.
Easy Maintenance – Simplifies repairs and replacements without cutting pipes.
Customizable – Available in various sizes, materials, and configurations.
- Applications of Pipe Couplings
Pipe couplings are widely used across industries due to their versatility, strength, and leakproof performance:
Industrial Plumbing – Firefighting systems, HVAC, and compressed air lines.
Marine & Offshore – Freshwater and seawater piping on ships and oil rigs.
Power Plants – Cooling systems, lubrication lines, and steam pipes.
Automotive – Exhaust system connections (muffler couplings).
Construction – Water supply, gas distribution, and structural piping.
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What’s the difference between a full coupling and a half coupling?
A full coupling joins two pipes of the same size, while a half coupling connects a pipe to a larger vessel or main line.
Q2: Can pipe couplings handle highpressure systems?
Yes, highquality threaded or compression couplings are designed for highpressure applications.
Q3: How do I choose the right coupling material?
Consider fluid type, temperature, pressure, and environmental conditions. For example:
Stainless steel for corrosive fluids.
PVC for chemical resistance and lowcost plumbing.
Q4: Are pipe couplings reusable?
Some (like compression couplings) can be reused, while welded or glued couplings are permanent.
Q5: Where can I find reliable pipe couplings?
Reputable suppliers offer carbon steel, stainless steel, and PVC couplings in various sizes.
- Conclusion
Pipe couplings are indispensable components in modern piping systems, enabling secure connections, repairs, and modifications. With options ranging from stainless steel to PVC, they cater to diverse industrial, marine, and residential needs.
Choosing the right type and material ensures longlasting performance, minimizing leaks and maintenance costs. Whether for plumbing, manufacturing, or automotive use, highquality couplings enhance efficiency and reliability in any piping network.











